Back
Painful Sex in Women: Obturator Internus
By Shannon Strauch, PTA, STMT-1 on 3/28/2024

Experiencing painful sex due to obturator internus tightness can be a complex issue that requires understanding and targeted treatment. Here are some insights into this condition:
Understanding Obturator Internus Muscle:
The obturator internus muscle is located deep within the pelvic floor and plays a role in stabilizing the pelvis and supporting pelvic organs.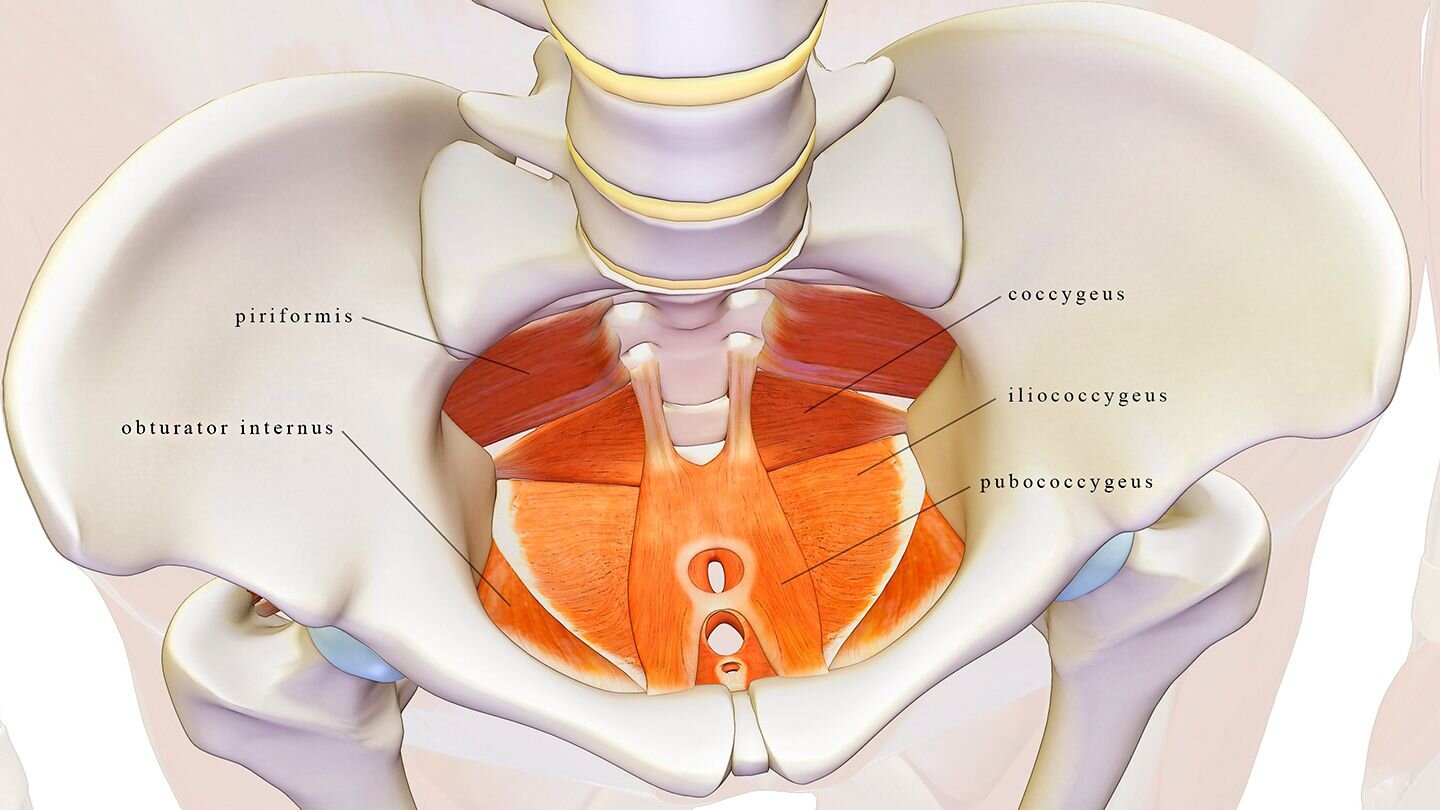
The obturator internus also forms Alcock's Canal, which the pudendal nerve travels through. Alcock's canal, also known as the pudendal canal or pudendal sheath, is an important anatomical structure in the pelvic region that houses the pudendal nerve and associated vessels. Here's an overview of Alcock's canal anatomy:
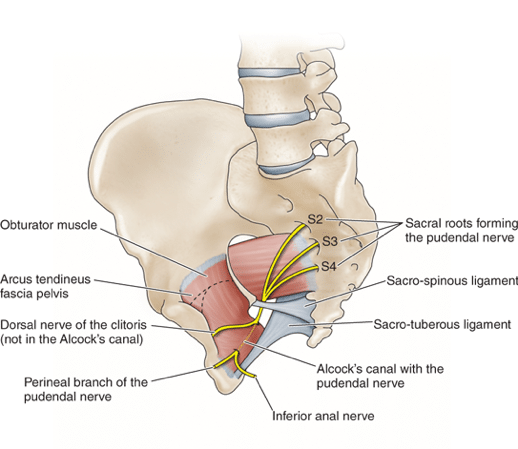
Location:
Alcock's canal is located in the pelvic floor, specifically in the ischioanal fossa. It runs along the medial aspect of the ischium, which is one of the bones of the pelvis.Contents:
The primary contents of Alcock's canal include:Pudendal Nerve: This nerve provides sensory and motor innervation to the perineum, including the external genitalia, anal region, and associated muscles (such as the anal sphincter and perineal muscles).
Pudendal Artery: A branch of the internal iliac artery, the pudendal artery supplies blood to the perineum, genitals, and associated structures.
Pudendal Vein: Veins accompanying the pudendal artery.
Function:
Alcock's canal plays a crucial role in the innervation and vascular supply of the pelvic floor and perineum. The pudendal nerve is especially important for maintaining sensation and muscle function in these areas.Clinical Relevance:
Alcock's canal is relevant in various medical conditions, including pelvic floor dysfunction, perineal pain syndromes, and sexual dysfunction. Compression or irritation of the pudendal nerve within the canal can lead to symptoms such as pelvic pain, numbness or tingling in the genitals or perineum, and pain during sexual intercourse.
Symptoms:
Tightness or dysfunction in the obturator internus muscle can lead to symptoms such as pain or discomfort during sexual intercourse, deep pelvic or hip pain, and difficulty with certain movements.Causes:
Several factors can contribute to obturator internus tightness, including childbirth trauma, repetitive strain injuries, overuse, poor posture, pelvic floor dysfunction, and certain medical conditions like endometriosis or pelvic inflammatory disease.Diagnosis:
Diagnosis typically involves a thorough physical examination by a healthcare provider, often including pelvic floor specialists or physical therapists. Imaging studies like MRI may also be used to assess muscle function and structure.Treatment Options:
Treatment for painful sex due to obturator internus tightness may include:Pelvic Floor Physical Therapy:
This focuses on exercises to strengthen and relax pelvic floor muscles, improve flexibility, and address muscle imbalances.
Manual Therapy:
Techniques like massage, myofascial release, and trigger point therapy can help release tension in the obturator internus muscle.
Stretching and Relaxation Techniques:
Specific stretches and relaxation exercises can target the obturator internus muscle and promote muscle relaxation.
Self-Care Strategies:
Patients can also incorporate self-care strategies into their routine, such as practicing deep breathing exercises, using heat packs, maintaining good posture, and avoiding activities that exacerbate symptoms.Follow-Up and Monitoring:
It's important for individuals with painful sex due to obturator internus tightness to follow up with their healthcare providers regularly to monitor progress, adjust treatment as needed, and address any new symptoms or concerns.
By addressing the underlying causes of obturator internus tightness and implementing targeted treatments, many individuals can experience relief from pain during sex and improve their overall pelvic health.
Read More:
Dry Needling for C-Section Scars and Postpartum Recovery By Dr. Christine Martirez PT, DPT on 10/15/2024 Learn how dry needling can be used for c-section scars and c-section recovery How Red Light Therapy Can Be Used to Treat Pelvic Floor Dysfunctions By Dr. Christine Martirez PT, DPT on 10/15/2024 Learn about red light therapy and how it can be used to treat pelvic floor dysfunctions
Are you ready to live pain free?
Request An Appointment