Back
Why do I have painful erections? Why do I have painful ejaculations?
By Shannon Strauch, PTA, STMT-1 on 1/27/2024
Painful erections or ejaculation can be concerning for men, for obvious reasons. It's essential to consult with a healthcare professional who can conduct a thorough examination, take a detailed medical history, and perform any necessary tests to determine the underlying cause of your symptoms. What are some possible causes for pain
Infections:
Infections of the urinary or reproductive system, such as prostatitis or a urinary tract infection, can lead to pain during erections and ejaculation.Inflammation:
Inflammation of the prostate (prostatitis) or other reproductive organs can cause discomfort during sexual activities.Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs):
Certain STIs, such as chlamydia or gonorrhea, may cause pain during erection and ejaculation. It's crucial to get tested for STIs if you are sexually active.Trauma or Injury:
Injury to the genital area or trauma during sexual activity can result in pain during erections and ejaculation.Psychological Factors:
Stress, anxiety, or other psychological issues can sometimes manifest as physical symptoms, including pain during sexual activities.Prostate Issues:
Conditions like an enlarged prostate (benign prostatic hyperplasia) or prostate cancer may lead to painful erections and ejaculation.Nerve Damage:
Damage to the nerves in the pelvic region can cause pain during sexual activities.Medication Side Effects:
Some medications may have side effects that include sexual dysfunction or pain during ejaculation.
Once you have been tested to rule out any active infection, this is where a trained Pelvic Floor Physical Therapist can come in. If your painful erections or painful ejaculation are related to pelvic floor dysfunction, muscle tension, or issues with the pelvic organs, a Pelvic Floor PT will be able to perform:
Manual Therapy:
Hands-on techniques to release tension and improve muscle function.Muscle Tension and Relaxation:
Pelvic floor therapists can teach relaxation techniques to address muscle tension in the pelvic floor. This can be beneficial if excessive muscle tightness contributes to pain during ejaculation.Biofeedback:
Using sensors to provide visual or auditory feedback to help you gain awareness and control of pelvic floor muscles. Biofeedback may be used to help individuals gain awareness and control over their pelvic floor muscles. This can be particularly useful for conditions where muscle coordination plays a role.Exercises:
Prescribing specific exercises to strengthen or relax the pelvic floor muscles.Education:
Providing information about pelvic anatomy, proper body mechanics, and lifestyle factors that may contribute to symptoms.
Possible Reasons for Painful Erection, Painful Ejaculation, or Painful Orgasm in Men- Pelvic Floor Therapy
Symptoms of inflammation, infected, or an enlarged prostate (prostatitis, BPH) can include pain in the back, frequent urination, difficulty urinating, or painful ejaculation. Pelvic Floor Therapy can help reduce tightness in the pelvic floor affecting the prostates ability to perform its duties as a lymphatic organ and help decongest the pelvic floor by using manual therapy techniques, stretching, and teaching the pelvic floor muscles how to properly contract and relax.
Trauma to the pelvic region can cause damage to muscles or nerves. A pelvic floor therapist will be able to assess the injury the same as an orthopedic injury to help return to painless sexual function.
Peyronie's disease is a condition characterized by the development of fibrous scar tissue, known as plaques, within the penis. These plaques can cause the penis to bend or curve during erections, leading to pain, deformity, and, in some cases, difficulty with sexual intercourse. A pelvic floor therapist can educate a patient on proper stretches to perform to reduce this penile tension
General muscle tightness or dyssynergy of the pelvic floor muscles can make it difficult for an erection or to reach ejaculation. A pelvic floor therapist can use manual therapy techniques, educate patients on proper stretching and breathing techniques, stimulate the Vagus nerve to calm down the nervous system out of "fight or flight" mode, and work on behavioral or postural changes
The pudendal nerve is a major nerve in the pelvis that plays a crucial role in the innervation of the genital and pelvic region. It arises from the sacral plexus, which is a network of nerves originating from the sacral spinal cord (S2-S4). The pudendal nerve has both sensory and motor functions and is responsible for controlling and providing sensation to various pelvic structures.
Here is a general overview of the pudendal nerve pathway:
Origin:
The pudendal nerve originates from nerve roots S2 to S4 in the sacral spinal cord.Exit from Pelvis:
The nerve exits the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen, passes below the piriformis muscle, and re-enters the pelvis through the lesser sciatic foramen.Pelvic Floor:
Within the pelvis, the pudendal nerve gives off branches that innervate the pelvic floor muscles, including the external anal sphincter and the muscles of the perineum.Sensory Innervation:
The pudendal nerve provides sensory innervation to the genital area, including the penis and scrotum in males and the labia majora and minora in females. It also innervates the perianal region.Motor Function:
The nerve has motor branches that control the external urethral sphincter, aiding in the voluntary control of urination.Pudendal Canal:
The pudendal nerve passes through the pudendal canal, which is a tunnel formed by the obturator internus muscle. This canal is significant in protecting the nerve during its course.Termination:
The pudendal nerve terminates in the perineum, providing sensory and motor innervation to the external genitalia.
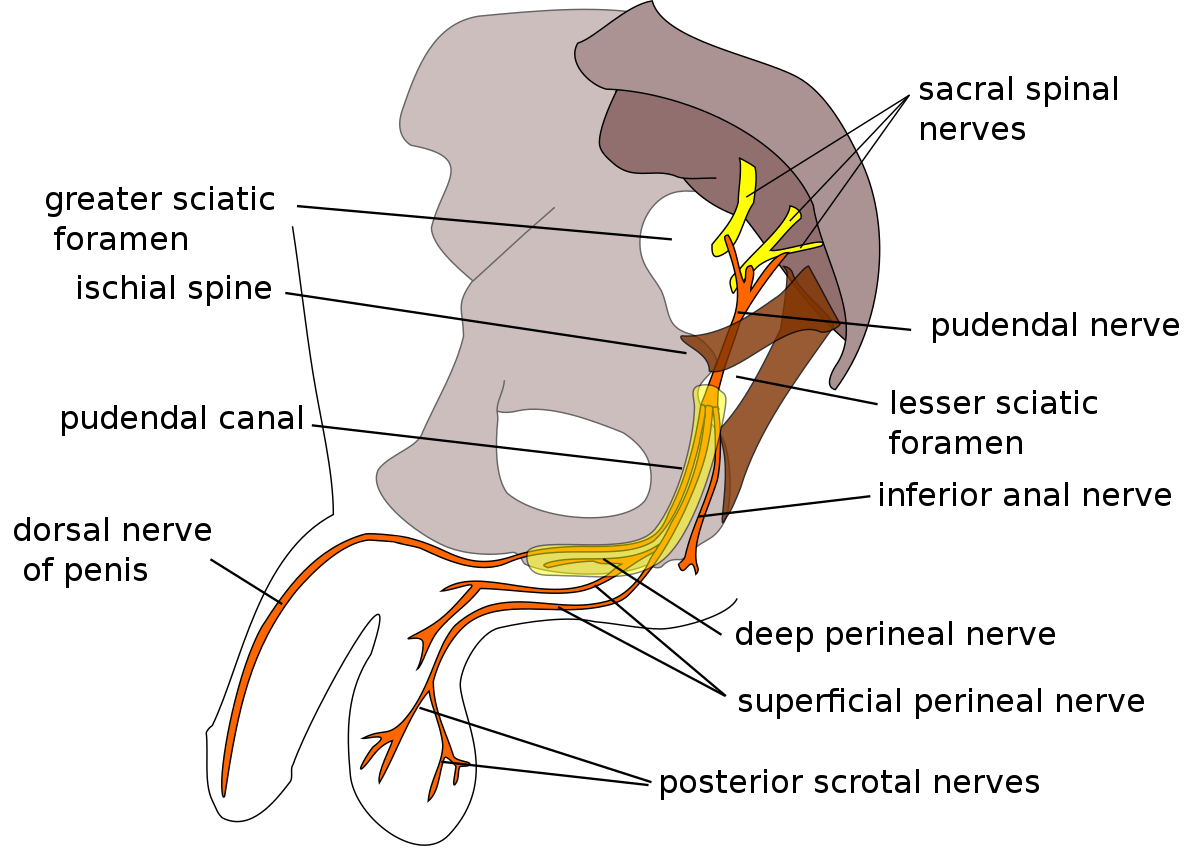
The pudendal nerve is crucial for various pelvic functions, including bladder and bowel control, sexual function, and sensation in the genital area. Dysfunction or compression of the pudendal nerve can lead to conditions such as pudendal neuralgia, which may result in pain, discomfort, or other sensory and motor disturbances in the pelvic region. This may include painful erection, painful ejaculation, or painful orgasm in men. Here at Pelvic Health, a thorough orthopedic assessment of the spine, sacrum and hips will give us a clearer picture as to where the pain is originating from and how it can be treated.
If you or someone you know has had a recent change in sexual function causing painful erection and-or painful ejaculation, reach out to us at Pelvic Health! 908-443-9880
Read More:
Dry Needling for C-Section Scars and Postpartum Recovery By Dr. Christine Martirez PT, DPT on 10/15/2024 Learn how dry needling can be used for c-section scars and c-section recovery How Red Light Therapy Can Be Used to Treat Pelvic Floor Dysfunctions By Dr. Christine Martirez PT, DPT on 10/15/2024 Learn about red light therapy and how it can be used to treat pelvic floor dysfunctions
Are you ready to live pain free?
Request An Appointment